Adaptive Missile Guidance Using GPS
Abstract
The name adaptive means; we can direct any missile using GPS in any vital conditions. GPS guided missiles have high exceptional navigational and surveying abilities. After GPS being launched, the warheads could be delivered to any part of the globe using the border of the onboard computer in the missile with the help of GPS satellite system. GPS allows accurate targeting of various military weapons including ICBMs, cruise missiles, and precision guided weapons. Weaponry projectiles with embedded GPS receivers able to endure accelerations of 12,000 G have been developed for use in 155mm. A range of techniques, most particularly narrow correlation spacing, has been developed to mitigate multipath errors. The multipath effects are much less severe in moving vehicles. Which means, when the GPS aerial is moving, the false solutions using reflected signals rapidly fail to cover and only the direct signals result in steady solutions.
Introduction
Missile guidance systems have evolved at a great rate over the past decades. The recent breakthrough technologies ensure that smart warheads will have increasing role to maintain military superiority. The main missile guidance concerns are mostly dependent when the missile receives its commands to move a certain path to reach the target. However for some missiles, these commands are generated via the missile computer autopilot. On the other side the commands are transmitted to the missile by some external sources. The missile seeker or sensor is a component within which the missile data is generated to feed into the missile computer. This data is processed by the computer and then used to generate the guidance commands. Today, we can see the sensor types that are commonly used to include infrared, radar, and the global positioning system. Depending on the relative position between the missile and the target at any given point in flight, the computer’s autopilot send commends to the control surfaces to adjust the missiles course.
The Radar guidance systems detect home and other targets by sensing electromagnetic energy reflected from the target's surface. The source of a reflected radiation is a radar transmitter, and the instance of weapons with active radar guidance, you can see this transmitter situated within the missile and in some cases of semi active guidance it will be carried out by the launch of aircraft. On other side the transmitter must beam electromagnetic radiation at the target level, so this radiation will travel to reach the target, reflect and then travel back receiving the antenna of the missile, be amplified, demodulated and analyzed to decide the course of the target, with the help of this information, it enables the guidance of the computer to guide the weapon towards the target to achieve a kill. A successful weapon will have the ability to discriminate the target's return and reflections from its background.
A wire-guided missile is a type of missile that is guided by signals sent to it via thin wires which are connected between the missile and its guidance mechanism; that is located somewhere near the launch site. The time missile flies these wires will be reeled out behind it. This system is most usually used in anti-tank missiles; where its ability is used in areas of limited line of view to make it useful. However the longest range of wire guided missiles in recent use is limited to about four kilometers. But the Tube launched, optically tracked wire guided missile system, (TOW) has a range of 3,750 meters but it would be improbable to be used at extreme range.
The Necessity
The previous guided missiles need to be delivered within a certain range of the target to make them released. Sometime the early guided missiles will be affected due to bad weather, physical phenomena or air current. A wire guided missile will have certain limitations of distance and the distance is limited for about 4 kilometers or less than it.
To avoid such limitations of early guided missiles the new technologies are used to guide the missile, through which the target does not get affected by the harsh weather conditions.
Types of Missile Guidance
- Using Radar
- Using Wires
- Using Laser
- Using GPS
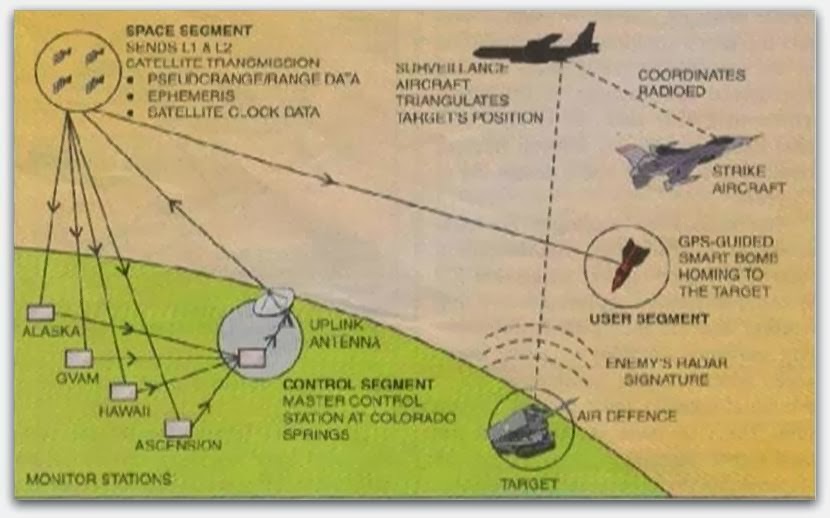
MISSILE GUIDANCE USING GPS
The vital idea behind designing GPS guided weapons is that of to use the 3-axis gyro/accelerometer package related to the reference for the weapon's autopilot, and correcting the accumulated flow errors related to the package using GPS PPS/P-code.
Such weapons are designated as ‘accurate’ ammunitions as they offer CEPs (Circular Error Probable) of the order to check the accuracy of GPS P -code signals, typically about 40ft. The next step is to upgrade the weapon before launch with a DGPS resulting position approximation; as this will allow it to correct the GPS errors when it flies to the target. Such weapons are designed precisely and will offer accurate results greater than laser guided weapons, potentially CEPs of several feet.
In order to support aircraft ammunitions it requires a DGPS receiver, a GPS receiver interfaces on its multiple ejector racks or pylons to download the target so that the launch point coordinates to the weapons easily. To defeat the disadvantages of laser guided missiles that present in unsuitable atmospheric conditions the radar guided missiles enters through a GPS method of navigating the missile to the target.
The development of GPS is purely related to the guided munitions that produce substantial changes in how air warfare is conducted. Unlike a laser-guided weapon, a GPS weapon does not need a launch aircraft remain in the environs of the target to light-up it for guidance - GPS/related weapons are of true fire-and-forget weapons. However, if these weapons are once released, they will wholly autonomous, and all weather capable with no degradation in accuracy; but, existing precise weapons require an covered line of sight between the weapon and the target for the optical guidance to work.
ADVANTAGES
- Navigation System Timing and Ranging (NAVSTAR). The GPS is now available in any weather, at any time, and any place on or above the earth. The navigation system for timing and ranging also provides precise time within a millionth of a second to synchronize the atomic clocks used in various military applications.
- GPS is even used to locate the present position of living and nonliving things; this is the famous concept which is used in “GOOGLE EARTH”.
- Military GPS has been integrated into user equipment like fighters, bombers, tankers, helicopters, ships, submarines, tanks, jeeps, and soldiers' equipments too.
- Furthermore it is included in the basic navigation activities for military applications which include target designations of cruise missiles and precision-guided weapons and close air support.
- The government controls the GPS receiver exports in order to prevent the GPS interception by the enemies .
- GPS satellites also can contains nuclear detonation detectors.
FUTURE SCOPE
Depending upon the future activities (i.e., navigation or precise target location), a particular kind of GPS can be used. It is thus summarized that the GPS based weapon systems are ready to stay in and will act as the backbone for the future development scope for more accurate and deadly munitions.
CONCLUSION
However the GPS guided weapons are not affected by bad weather conditions or limited to a wire, nor do they leave the gunner vulnerable for attack. GPS guided weapons are going to be the superior weapons of choice in modern day warfare with their technological advances over previous.