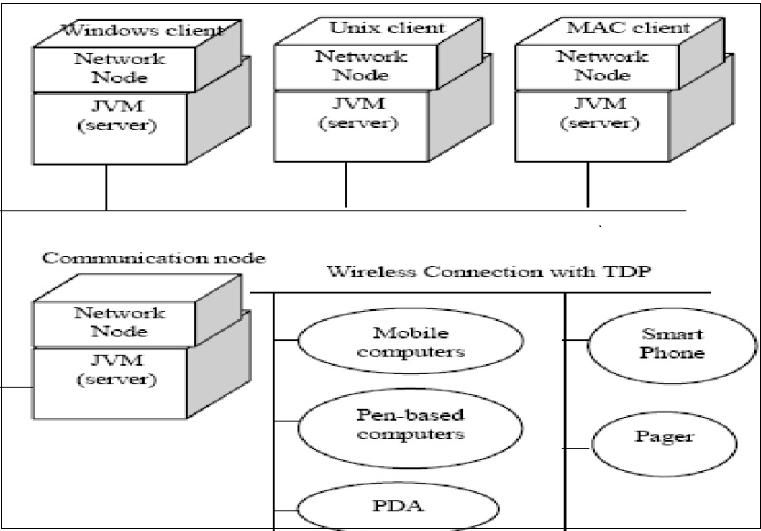
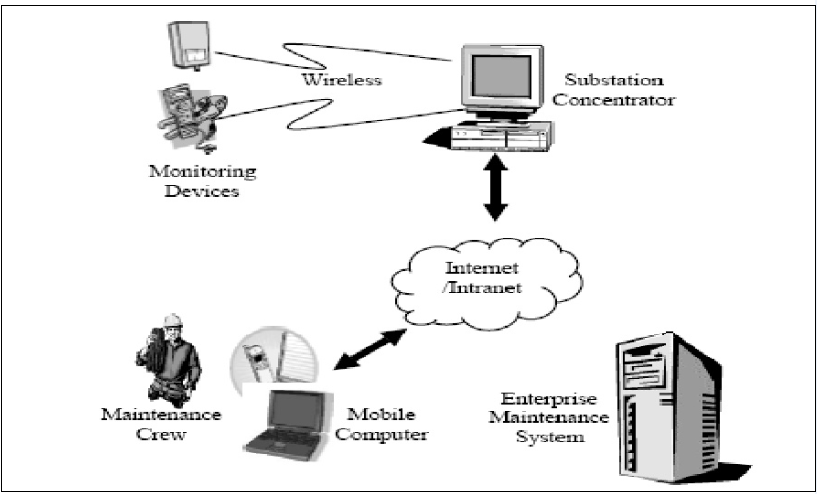
Circuit Breaker Maintenance by Mobile Technology
Abstract
Circuit breakers are critical components for power system operations. They play a vital role in switching the routine network protection and operation of other devices in power systems. To make sure that the circuit breakers are in good condition, periodical inspection, and preventive maintenance should be performed on time. The maintenance schedules should be on the routine recommendation of circuit breaker vendors. The currently modified time and maintenance strategy and the new emerging condition-based strategies require a flexible information processing techniques and software architecture.
Let us look how mobile software will help circuit breaker maintenance and repair tasks.
Introduction
The maintenance techniques and new methodologies are emerging while the circuit breakers keep improving in their designs and functionalities. For example, some new circuit breakers have rooted the monitoring instruments that are available to measure the coil current profiles and the operation timings. With the help of recorded information, you can monitor the condition of each breaker during its operation. This approach helps you to be more appropriate in replacing the time-directed for maintaining the condition directed by maintenance practice. When applied properly both maintenance cost and the maintenance crew are reduced. Since the number of circuit breakers in a power system is usually very huge, a small maintenance cost saving per each circuit breaker can build up a considerable benefit for the complete system. A more methodical solution; Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM), can be used to select the most suitable maintenance strategy.
The time when maintenance is scheduled, the maintenance crew need to access information distributed across the utility and storage using different data formats. By equipping the crew with new access methodology and to replace the old procedures like paper-based information exchange and logging method, the efficiency may be improved in very less time and it can be spent on preparing, reporting and logging. The information access method is capable of handling heterogeneous information sources and will be helpful to attain the goal. Also, this method should be secure and be available to work on unreliable public networks.
The mobile software provides a flexible framework for mobile agent applications; a mobile agent application program can travel through the intranet or internet to the computers where the mobile agent server or transporter is running. The mobile agent supports Agent Collaboration, Distributed Events, and Service Bridge. Compared with client-server systems, it can also process the data locally and thus decrease the network traffic. In addition, the Java platform encapsulates the network layer from the agent to make the programming easier. The mobile software can easily fit well in the circuit breaker maintenance scenarios.
Circuit Breaker Maintenance Tasks
The maintenance of circuit breakers deserves a special deliberation because of their importance for routine switching and for protecting other equipment. Electric broadcast system breakups and equipment obliteration can occur when a circuit breaker fails to operate, and this can be because of lack of a defensive maintenance. The need for maintenance of circuit breaker is often not clear as circuit breakers may be idle, open or closed, for long periods. Breakers when to remain idle for six months or more than six months should be open or close several times in series to verify proper operation and to remove if any accretion of dust or moving parts and contacts hits.
Circuit breakers consist the interrupter assembly; contacts, arc interrupters and arc chutes, operating mechanism, control panel, sealing system, operation rod, and breaking medium. To make sure the performance of a circuit breaker and all the components are kept in good condition; therefore, the preventive maintenance time should be widely adopted. The preventive maintenance tasks include periodic check, analysis, and replacement of damaged components and lubrication of the automatic parts. These maintenance intervals are usually determined using experiences or through next recommended schedules provided by the standards or vendors.
These maintenance practices are divided into three categories: remedial maintenance, preventive maintenance, and predictive maintenance.