Smart Antennas
A smart antenna is a digital wireless communications antenna system that takes benefit of multiplicity effect at the source- transmitter, the destination receiver, or both. Assortment effect involves the transmission and or reception of multiple radio frequency (RF) influence to increase data speed and reduce the error rate.
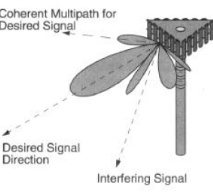
While in conventional wireless communications, a single antenna is used at the source, and another antenna is used at the destination. This is called SISO- single input, single output. Such systems are defenseless to problems caused by multipath effects. When an electromagnetic field is met with obstructions such as hills, canyons, buildings, and utility wires, the wave fronts are spread, and thus they take many paths to contact the destination. The late arrival of scattered portions of the signal causes troubles such as fading, cut-out and irregular reception (picket fencing). In a digital communications system like the Internet, it can cause a decrease in data speed and an increase in the number of errors. Thus the use of smart antennas can reduce or abolish the trouble caused by multipath wave propagation.
Smart antennas fall into three major categories; SIMO -single input, multiple output, MISO -multiple input, single output, and MIMO- multiple inputs, multiple outputs. In SIMO technology, one antenna is used at the source, and two or more antennas are connected at the destination. In MISO technology, two or more antennas are used at the source, and one antenna is connected to the destination. In MIMO technology, multiple antennas are engaged at both the source and the destination. MIMO has attracted the most attention recently because it can not only eliminate the adverse effects of multipath propagation but in some cases can turn it into an advantage.
Cons &Pros
Both beams smart and adaptive arrays offer high efficiency and thus high power for the preferred signal. When a large number of antenna elements are used at a higher frequency, Beam Smart antennas use narrow pencil beams. Thus high efficiency is obtained in the direction of the desired signal. If a fixed number of antenna elements are used the same amount times the power gain will be produced with the help of adaptive array antennas.
Another benefit is in the amount of meddling that is concealed. Beam smart antennas suppress it with the narrow beam and adaptive array antennas suppress the interfering by adjusting the beam pattern.
-
Cost
The cost of such a device will be additional, not only in the electronics section, but also in the power. That is the device is way too expensive, especially when you opts for MIMO methods, and this will also sometime decrease the life of battery of mobiles. However, the receiver chains that are used must be reduced in order to reduce the cost. Also the costs rise up due to the RF electronics and A/D converter used for each antenna.
-
Size
These types of methods are efficient in the large base stations. This will increase the size. Apart from this multiple external antennas are needed on each terminal. This is not practical, but companies are trying to adopt these methods like dual polarization to reduce the size.
-
Diversity
When multiple mitigations are required, then diversity becomes a big problem. The terminals and base stations must have multiple antennas. There are mainly three types of diversities. They are spatial, polarization, and angle.
Spatial separation of the antennas that are used is practically impossible when it is applied on mobile phones. It is also difficult to be achieved in point-to-point systems where a near line-of-sight exists between the transmitter and receiver. By using polarized diversity, the above problem can be avoided to a certain point. Dual polarization can be easily instigated without the use of spatial separation.
Angular diversity is the most commonly used method nowadays. The signals which have the maximum signal power are selected from multiple beams and are used to maintain diversity. But the gain depends on the angular spread. That is, if the spread is small, the diversity will also be small.
- Spatial-temporal processing
- Tracking
- Hooks in international
- Vertical integration
- Standards to include provisions for smart antennas